January 18, 2024 • Insights

Teachers hold an immensely important role in shaping the minds of future generations and contributing significantly to society. However, recent statistics indicate that the teaching profession is facing a crisis. There are currently 567,000 fewer educators in America’s public schools today than there were before the pandemic, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. Nationally, the ratio of hires to job openings in the education sector currently stands at 0.57 hires for every open position, according to BLS’s Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey (JOLTS).
A recent global study from The Education Endowment Foundation highlights the key factors that can help attract and retain teachers in the classroom: higher pay and a lighter workload.
On average, teachers suffer from a persistent “pay penalty” and make 20 percent less than other college graduates in different fields. “[This] financial penalty discourages college students from entering the teaching profession and makes it difficult for school districts to keep current teachers in the classroom,” says this report from the Economic Policy Institute.
According to Educators for Excellence, compensation does matter—and it should authentically reflect the work that educators put in. Seventy-eight percent of teachers have indicated that an improved salary would be a decisive factor in retaining them within the profession, thus reducing the need for administrators to attract and recruit new teachers—highlighting the mutually beneficial nature of raising teachers' pay. There are instances where educators earn even less in specific states, all the while being required to fulfill additional responsibilities beyond their contracted hours. The need for standardized teacher salaries nationwide is evident, underscoring the importance of recognizing and valuing the time teachers dedicate to their work. Modern time tracking software is one clear way to ensure that the extra time educators devote to their profession doesn’t go unnoticed or unrewarded.
Teachers Face Excessive Burnout and Stress
Educators face an unusual amount of stress, a reality that was sharply exacerbated by the pandemic. In 2022, teaching emerged as the top profession for burnout in a Gallup Poll. Female teachers, in particular, reported higher burnout rates compared to their male counterparts, with 55 percent of them feeling burned out. This is not surprising given the additional burdens teachers faced during the pandemic, including grading papers at home and covering classes due to substitute teacher shortages.
According to a more recent Education Week/Merrimack poll, 42 percent of teachers have reported that their teaching quality has been negatively impacted due to the state of their mental health. Disturbingly, over half of educators participating in the poll expressed that their mental health and overall well-being have deteriorated in 2023 compared to previous years. This alarming trend underscores the critical importance of addressing teachers' stress and mental health concerns. A mere 2 percent of teachers indicated that their respective districts provide any form of support for mental health and wellness, leaving a substantial gap in much-needed resources.
It’s not just teachers’ mental health that is suffering—many children are also experiencing a mental health crisis in the wake of the pandemic. “More than half of teachers say that the current state of students’ mental health is hurting their ability to learn and socialize, as well as negatively affecting educators’ capacity to manage their classrooms,” says the EdWeek report.
The well-being of teachers directly influences the quality of education they provide to their students. High levels of stress and burnout can lead to decreased job satisfaction, reduced effectiveness in the classroom, and even contribute to attrition rates. Therefore, creating a supportive environment that recognizes and actively addresses teachers' mental health is not only a matter of their personal welfare but also a vital factor in sustaining a robust and vibrant education system. Providing accessible resources, counseling services, and programs that promote work-life balance can go a long way in alleviating the stress burden on teachers, ultimately benefiting both educators and students alike. (One program, edwell, offers personalized one-on-one coaching by experienced educator peers in a safe and supportive environment.)
The Statistics on the Teacher Exodus
The challenges faced by teachers are reflected in the statistics—according to this NEA report, a staggering 55 percent of educators are now considering leaving the profession earlier than planned. The reasons behind this exodus are varied, but a lack of support, an overwhelming workload, perceived disrespect from the general population, struggles with student behavior issues, and the mental health issues cited above are among the key factors pushing teachers to reconsider their careers.
The Education Week poll did reveal some good news: Overall teacher satisfaction is up 10 percentage points from last year. However, the situation remains concerning, with 35 percent of teachers expressing their likelihood to quit within the next two years. This figure includes not only those nearing retirement but also teachers who are new to the profession and are already feeling overwhelmed. The fact that 14 percent of teachers stated they were "very likely" to quit signals a clear breaking point among educators.
The difficulties in hiring new teachers exacerbate the crisis, with 86 percent of school districts reporting challenges in recruiting fresh educators, according to a report from Educators for Excellence. Moreover, only 43 percent of younger teachers (under age 30) express a likelihood of staying in the classroom for their entire career, indicating that the teaching profession is losing its appeal among the younger generation.
Diversity in the teaching workforce is crucial for fostering an inclusive learning environment. However, only 52% of BIPOC (Black, Indigenous, and People of Color) teachers express a likelihood to stay in the classroom, also according to Educators for Excellence. This statistic is particularly alarming, as it indicates that nearly half of BIPOC teachers are considering leaving the profession. While salary plays a part in this decision, BIPOC teachers also seek more professional development opportunities and support with housing, families, and healthcare. School districts must actively address these concerns to retain and attract diverse teaching talent.
The teacher shortage issue extends beyond just the teachers themselves. It affects various school staff members, including custodians, paraprofessionals, cafeteria workers, and even instructional coaches who are forced to fill in for absent teachers due to a shortage of substitutes. When schools are understaffed, educators struggle to fulfill their roles effectively, creating a cascading effect that impacts the quality of education.
Teacher Shortages by State
Teacher shortages vary across the country, and certain subject areas are more in demand than others. In many states, subjects such as special education, math, science, world languages, and early childhood education are most in need of qualified teachers. News Nation offers a state-by-state breakdown (as of the 2022–23 school year), including details about which states will accept out-of-state teaching licenses.
A 2022 EdWorkingPaper report revealed the following state breakdowns, with the states in dark blue reporting the most significant shortages:
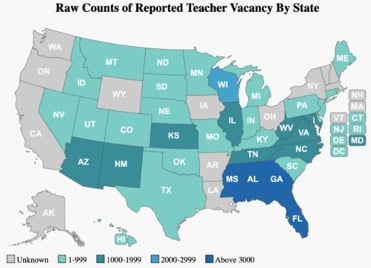
Source: Nguyen, Tuan D., Chanh B. Lam, and Paul Bruno. (2022). Is there a national teacher shortage? A systematic examination of reports of teacher shortages in the United States. (EdWorkingPaper: 22-631).
Using another method to assess the teacher shortage, Scholaroo, a scholarship search platform, compared the number of currently employed teachers in each state to the state population. View their interactive map here. Their research revealed that the states with the highest teacher-to-population ratio were, in order:
|
North Dakota |
|
Nebraska |
|
Vermont |
|
New Jersey |
|
Wyoming |
|
Texas |
|
Missouri |
|
Kansas |
|
New Hampshire |
|
Iowa |
The states with the greatest number of vacancies were:
|
North Carolina |
|
Tennessee |
|
Kentucky |
|
Arizona |
|
Washington |
|
Michigan |
|
Hawaii |
|
Nevada |
|
California |
|
Oregon |
|
Florida |
Local Headlines on the Teacher Shortage, and How Districts Are Combating it
GA: In the metro Atlanta area, state officials are expressing concerns about a teacher shortage just as students are heading back for the start of a new school year. As of July 2023, there were 400 teacher openings in DeKalb County, 195 vacancies in Gwinnett County Schools, and 100 certified teacher vacancies in Henry County Schools. Lisa Morgan, the President of the Georgia Association of Educators, said “There definitely is a teacher shortage; it is a growing problem. We are seeing districts having job fairs right up to preplanning and the beginning of the school year.”
CA: In California, “It has become so difficult to hire and retain educators that administrators [in the rural district of Alturas] have attended hiring fairs not just across California, but also in Montana, Nevada, New Mexico and Oregon,” reports the LA Times. Los Angeles Unified, one of the state's largest public school districts, lists more than 450 teacher vacancies for the 2023–24 academic year. To boost recruitment, LAUSD is offering a $5,000 stipend and 20 yearly hours of paid PD for new teachers who commit to remaining at a high-needs school for three years.
CT: Connecticut reports an urgent need for qualified teachers, particularly in four priority areas: Math, Science, Bilingual Education, and Special Education. The state is offering incentives such as the Teachers Mortgage Assistance Program, designed to alleviate shortages by making it easier for teachers to buy a home in the community in which they teach. Other tactics include flexible policies for the rehiring of retired teachers and cancellation of student debt for certain full-time teachers.
LA: As of August 2, 2023, Jefferson Parish schools reported 200 teacher vacancies—a number that has many concerned. "I want you to know this is a nationwide crisis," said Ricky Johnson, of the Jefferson Parish school board. The district is doing its best to recruit new teachers and implement stopgaps, even as students stream back into school. "There was just a meeting with the president of retired teachers. We are also working to get our non-certified teachers certified,” Johnson shared with local news outlet WDSU. “We are trying to grow our own in JP. Also working to try to find substitutes."
VA: Confronted by concerning teacher shortages, Virginia recently entered into a partnership with a for-profit online teacher-credentialing organization, reports USA Today. This collaborative effort aims to expedite the process of bringing additional teachers into classrooms, all while circumventing the elevated tuition expenses typically associated with conventional colleges and universities. The state had 3,500 full-time teacher vacancies during the 2022-2023 school year.
TX: The Brazosport Independent School District, an 11,500-student district outside of Houston, implemented an innovative plan to combat their persistent and ongoing need to fill more teaching positions. According to the Texas Tribune, the district “launched a unique ‘teacher apprenticeship’ program that allows aspiring teachers to earn a bachelor’s degree and teacher certification — at no cost. In return, the teachers have to work in the district for at least three years. The plan includes a paid residency program in which apprentices are paired with a teacher mentor and work with them in a classroom for a full school year.” Teacher residency models such as Brazosport’s offer a “promising long-term solution to meeting district hiring needs, allowing districts to play a direct role in training their future workforce,” says a Learning Policy Institute report.
What Else Can Be Done?
To make teaching a sustainable and attractive career choice, educators have noted specific areas where they need support. Sixty-two percent of teachers demand better support for discipline, according to Education Week, as managing student behavior is essential for effective classroom learning. Additionally, smaller class sizes are desired by 62 percent of teachers, as they recognize the positive impact on student-teacher interaction and individualized attention.
Teachers also suggest reducing administrative work and meetings, acknowledging their hard work, and allowing them to take time off, including mental health days, to better cope with the demands of the job. Moreover, the NEA reports that 92 percent of educators endorse the hiring of more support staff, such as paraprofessionals and playground aides, to assist in creating a conducive learning environment.
The state of the teacher shortage is a complex and multifaceted issue that requires immediate attention and action from educational authorities and policymakers. By offering higher salaries, bonuses, and lighter workloads, school districts can attract more teachers, particularly to challenging schools. Additionally, supporting educators with discipline, smaller class sizes, and acknowledgment of their hard work can improve retention rates. Emphasizing diversity and providing comprehensive support, both professionally and personally, can retain BIPOC teachers who bring valuable perspectives to the classroom. Finally, investing in support staff and addressing the concerns of young teachers will contribute to making the teaching profession more appealing and sustainable for generations to come. Only through collective efforts can we ensure that education thrives and that our future remains bright.
“I call on our policymakers, again, to value our nation’s educators and get serious about solving this problem,” said Becky Pringle, National Education Association President. “That means paying educators like the professionals they are, ensuring that their students can get the mental health supports they need…and addressing the staff shortages so our educators can do what they do best—help every student thrive.”
Make it easy for teachers to accurately track their time and record absences while simultaneously making it just as easy for you to find and assign substitutes. Red Rover combines modern employee absence management and modern employee time tracking, helping you save time and work cohesively to increase substitute fill rates, manage employee absences, and accurately handle employee time. Click here to schedule a demo!
Subscribe to get the latest Red Rover news and insights delivered straight to your inbox.
Red Rover builds best-in-class software solutions for mission-critical tasks in K-12 human capital management. Join 1,500+ school districts in the Red Rover revolution today.
We send occasional emails jam-packed with strategies, events, and insights delivered straight to your inbox!